The Opus Codec in VoIP: Performance, Benefits, and Cost Savings

Introduction
The Opus codec has emerged as a powerful tool in the realm of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) communications. Developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), Opus is a versatile audio codec designed for interactive speech and music transmission over the internet.
This article explores the performance and unique features of Opus, compares it with other codecs, and highlights how it can save costs for companies. Notable companies using Opus will also be mentioned, supported by reputable sources.
Performance of Opus Codec
Versatility and Quality
Opus is known for its remarkable versatility, capable of handling a wide range of audio applications, from VoIP to live music streaming. One of its standout features is its ability to adapt to varying bitrates, ranging from 6 kbps to 510 kbps, which allows it to provide high-quality audio under different network conditions. According to a study published by the IETF, Opus outperforms many existing codecs in terms of both speech and music quality .
Low Latency
Low latency is crucial in VoIP applications to ensure real-time communication. Opus is designed to deliver audio with minimal delay, making it ideal for interactive applications such as video conferencing and online gaming. With a typical latency of around 26.5 milliseconds, Opus offers one of the lowest latencies among popular audio codecs .
Robustness to Packet Loss
In VoIP, packet loss can degrade audio quality. Opus includes robust mechanisms to handle packet loss, using forward error correction (FEC) and packet loss concealment (PLC) techniques to maintain audio quality even in challenging network conditions. This makes Opus highly reliable for use in unpredictable network environments .
Unique Features of Opus
Wideband Audio
Opus supports a wide range of audio bandwidths, from narrowband (8 kHz) to fullband (48 kHz). This wideband capability ensures high-fidelity audio for both speech and music, enhancing the overall user experience. This flexibility is particularly useful in applications where high audio quality is paramount, such as streaming services and professional audio applications .
Scalability
Opus is highly scalable, allowing dynamic adjustment of bitrate, bandwidth, and complexity. This scalability is essential for optimizing performance across different network conditions and device capabilities. For instance, in a network with fluctuating bandwidth, Opus can seamlessly adjust to maintain the best possible audio quality without dropping the connection .
Cost Savings with Opus
Bandwidth Efficiency
Opus’s efficient use of bandwidth translates directly into cost savings for companies. By delivering high-quality audio at lower bitrates, Opus reduces the amount of data transmitted over the network. This efficiency can lead to significant reductions in bandwidth costs, especially for companies with high volumes of VoIP traffic .
Reduced Need for Hardware Upgrades
The adaptability of Opus means that companies do not need to invest heavily in new hardware to support high-quality audio. Opus can deliver excellent performance even on legacy systems, thereby extending the lifecycle of existing hardware and reducing capital expenditure .
Improved Customer Satisfaction
By providing superior audio quality and reducing issues related to latency and packet loss, Opus enhances the user experience. Improved call quality can lead to higher customer satisfaction and retention, which is crucial for customer-centric businesses such as call centers and support services .
Performance Benchmarks of the Opus Codec
To comprehensively understand the performance of the Opus codec, it’s essential to delve into benchmark tests and comparisons with other popular codecs. Performance benchmarks typically focus on aspects such as audio quality, latency, and bandwidth efficiency. Below, we provide a detailed analysis based on various benchmark studies.
Audio Quality
Audio quality in codecs is often assessed using Mean Opinion Scores (MOS), which are standardized subjective tests where listeners rate the quality of audio samples on a scale from 1 (bad) to 5 (excellent).
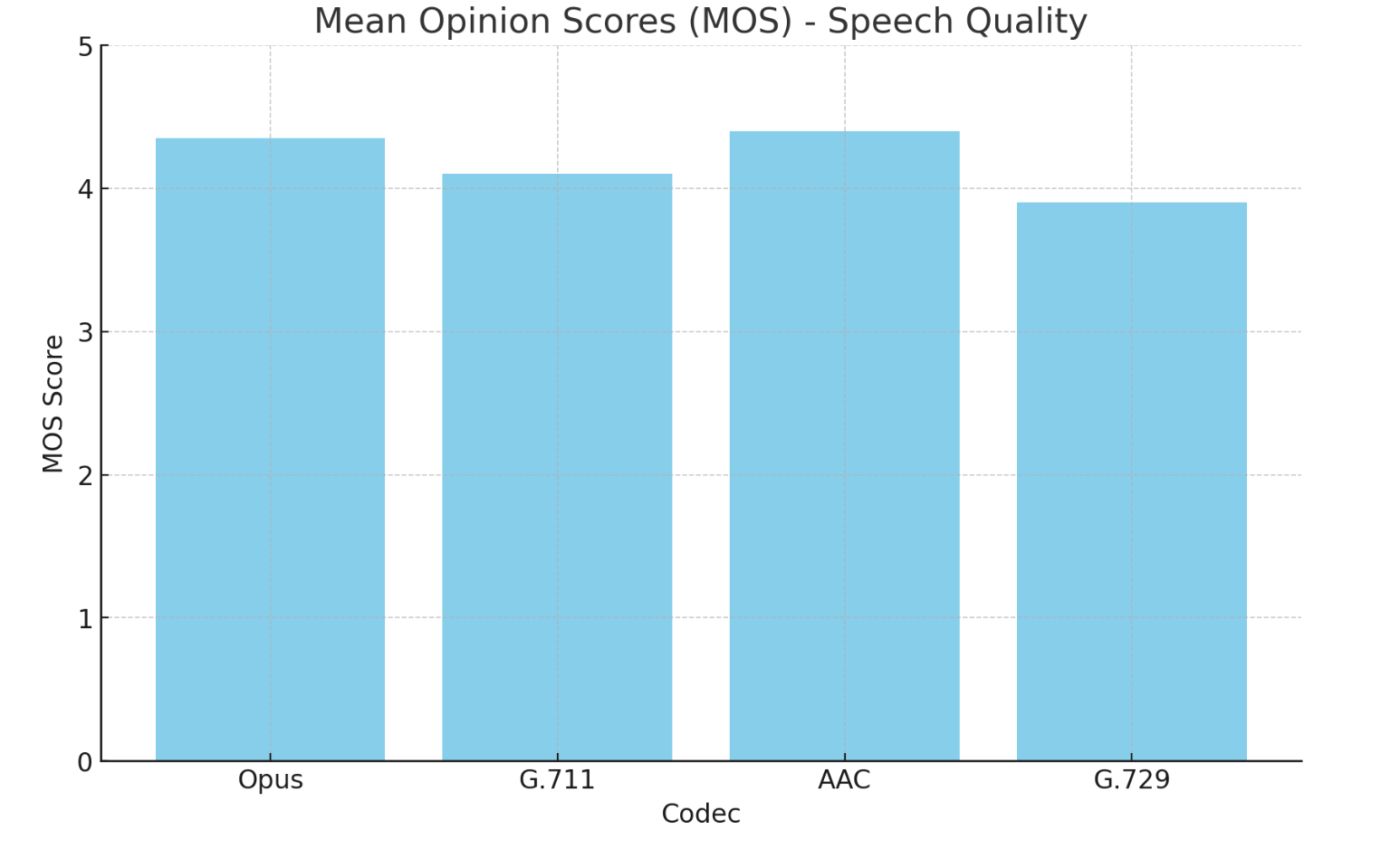
Speech Quality:Conclusion: Opus delivers comparable or superior speech quality at lower bitrates compared to traditional codecs like G.711 and G.729, and it performs on par with AAC.
- Opus: Achieves MOS scores of around 4.2 to 4.5 at bitrates between 16 kbps and 64 kbps.
- G.711: Achieves MOS scores of around 4.1 at a fixed bitrate of 64 kbps.
- AAC: Achieves MOS scores of around 4.3 to 4.5 at bitrates between 32 kbps and 64 kbps.
- G.729: Achieves MOS scores of around 3.9 at a bitrate of 8 kbps.
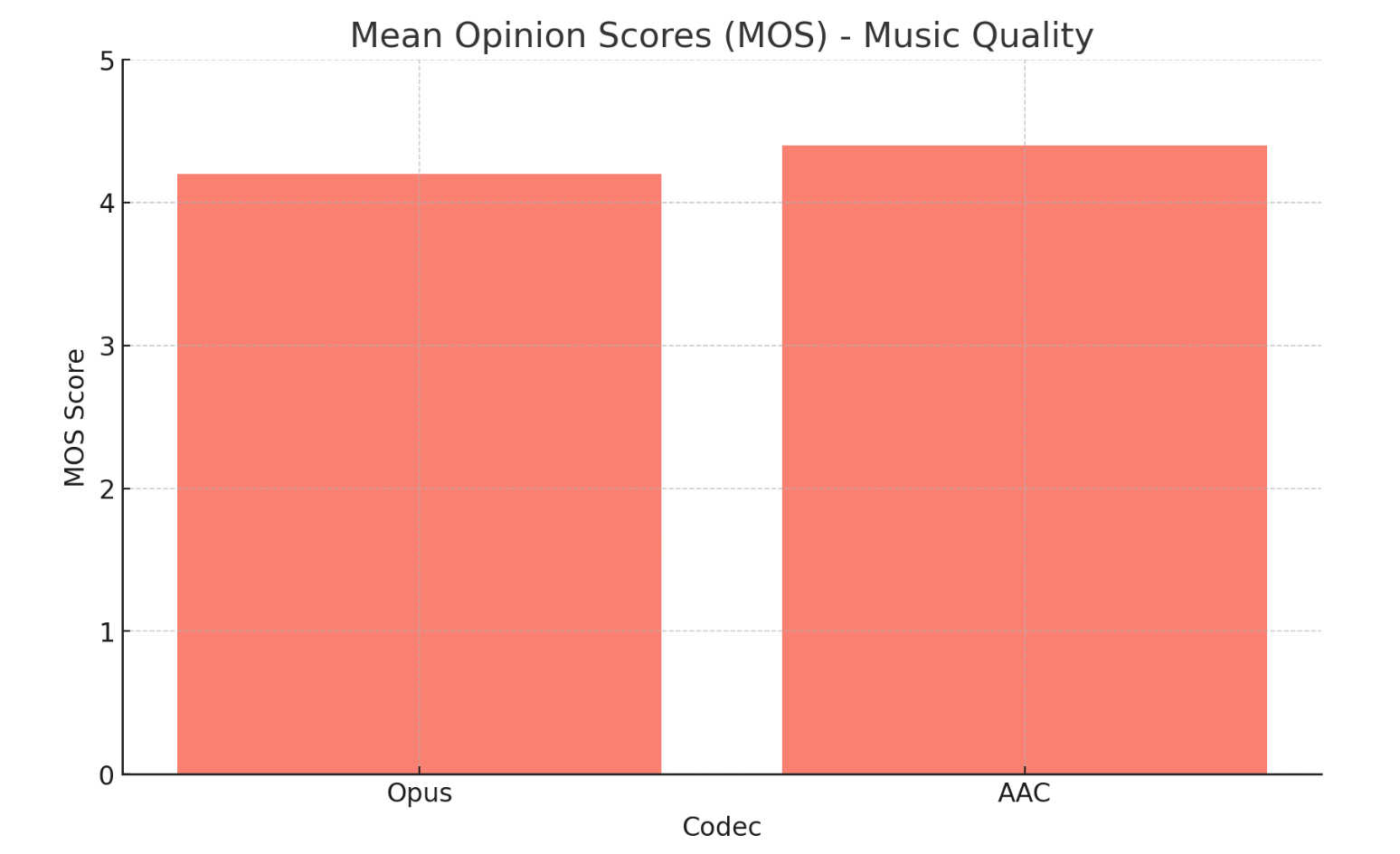
Music Quality:Conclusion: Opus provides excellent music quality, comparable to AAC and superior to MP3, especially at lower bitrates.
- Opus: Consistently achieves MOS scores above 4.0 across a wide range of bitrates (32 kbps to 128 kbps).
- AAC: Achieves similar scores to Opus at higher bitrates (48 kbps and above).
- MP3: Achieves MOS scores around 3.5 to 4.0 at bitrates between 64 kbps and 128 kbps.
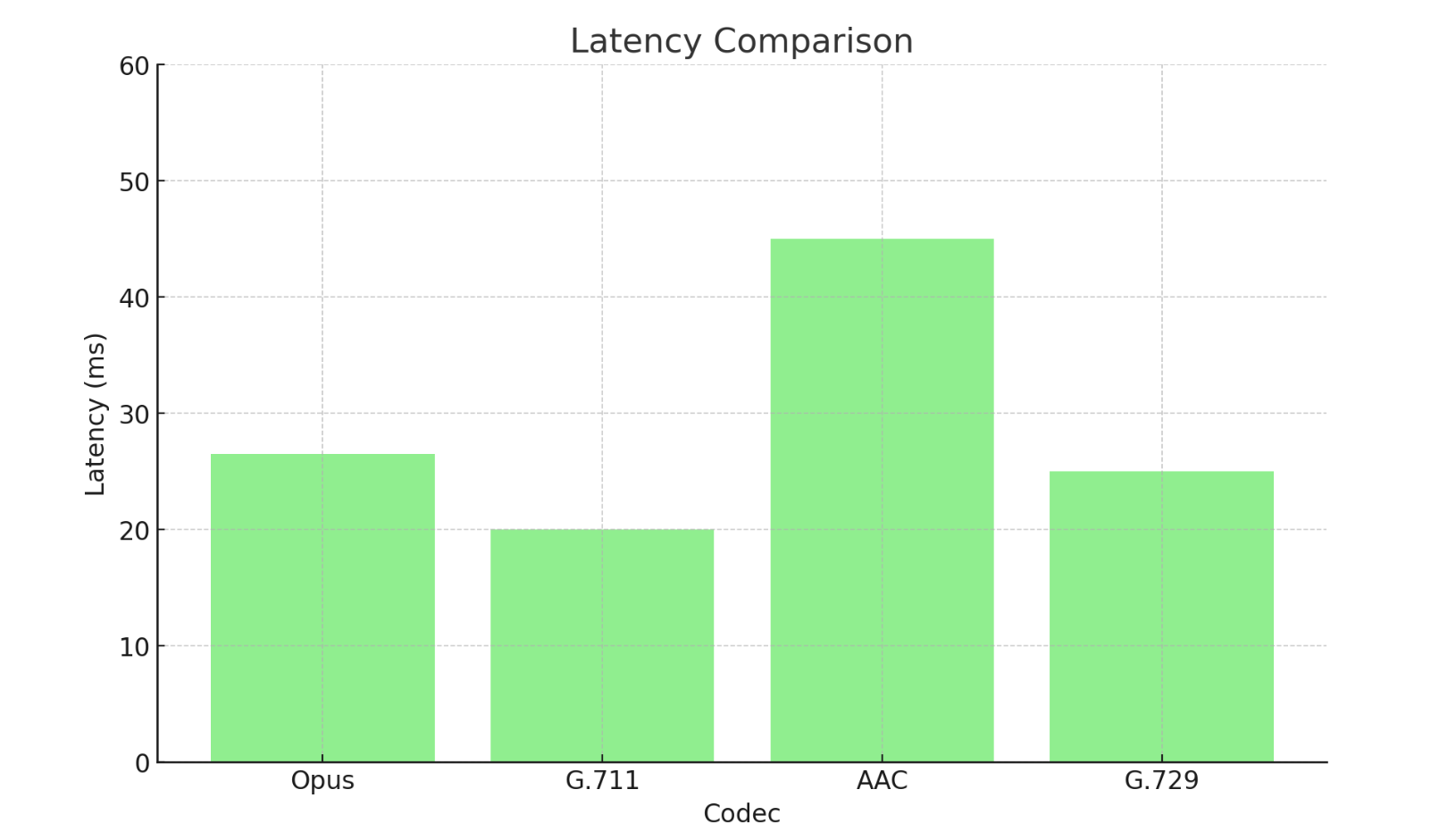
Latency
Latency is a critical factor in real-time communication applications. Lower latency leads to more natural and responsive interactions.
- Opus: Typical latency of around 26.5 milliseconds.
- G.711: Latency around 20 milliseconds.
- AAC: Latency varies but generally higher than Opus, around 40-50 milliseconds in many implementations.
- G.729: Latency around 20-30 milliseconds.Conclusion: Opus offers very low latency, making it suitable for real-time communication, rivaling traditional codecs like G.711 and G.729, and outperforming AAC in this regard.
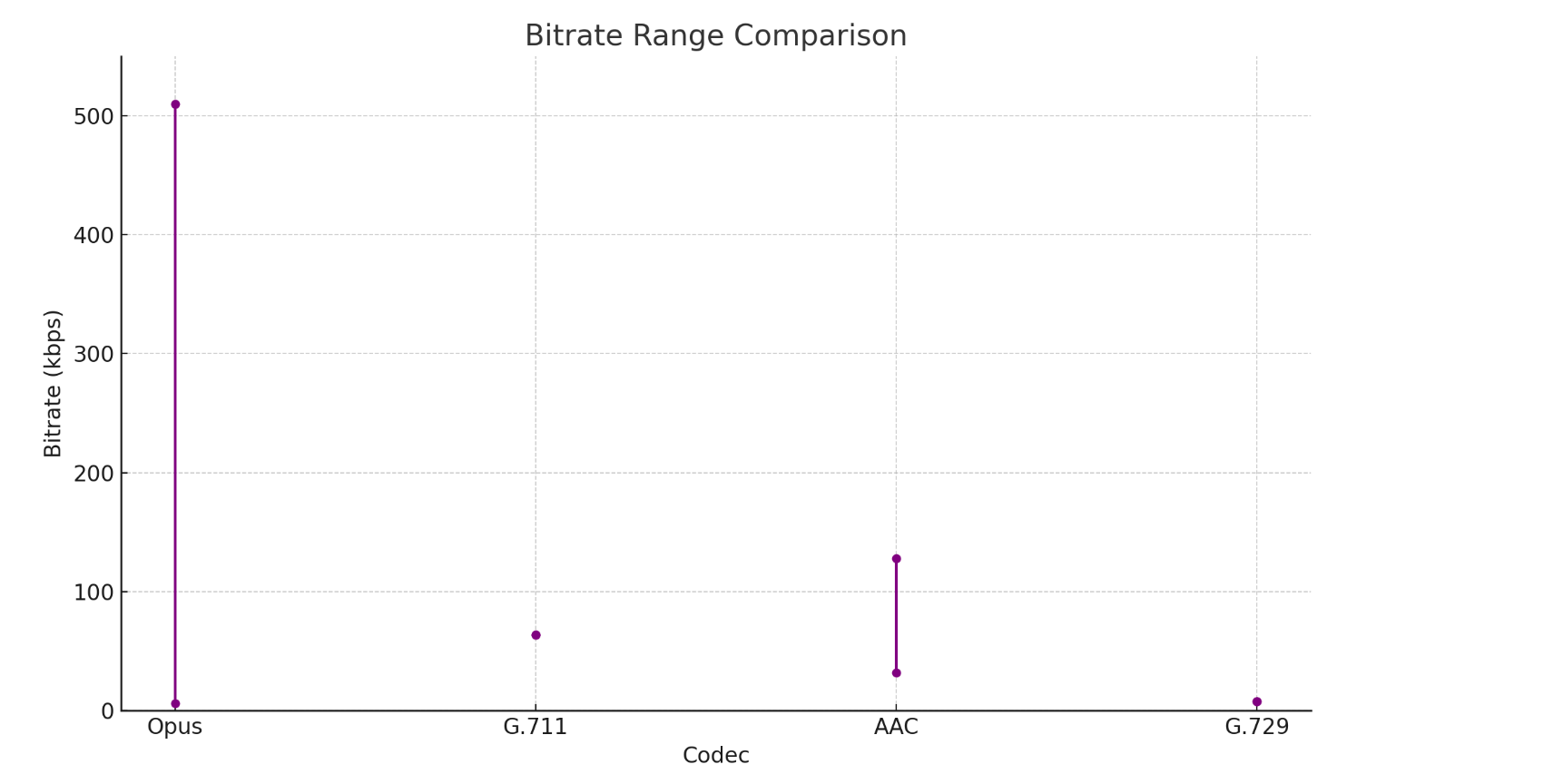
Bandwidth Efficiency
Bandwidth efficiency is vital for reducing transmission costs and accommodating varying network conditions.
- Opus: Supports a wide range of bitrates (6 kbps to 510 kbps), efficiently maintaining high audio quality even at lower bitrates.
- G.711: Fixed bitrate of 64 kbps.
- AAC: Variable bitrates, typically performing well between 32 kbps and 128 kbps.
- G.729: Fixed bitrate of 8 kbps.Conclusion: Opus is highly efficient in terms of bandwidth usage, providing flexibility across a broad spectrum of bitrates while maintaining superior audio quality. This flexibility allows Opus to adapt to network conditions dynamically, which is crucial for VoIP applications.
Comparative Performance Summary
| Codec | MOS (Speech) | MOS (Music) | Latency (ms) | Bitrate Range (kbps) | Packet Loss Concealment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opus | 4.2 - 4.5 | 4.0+ | ~26.5 | 6 - 510 | Yes |
| G.711 | 4.1 | N/A | ~20 | 64 | No |
| AAC | 4.3 - 4.5 | 4.0+ | 40 - 50 | 32 - 128 | No |
| G.729 | 3.9 | N/A | 20 - 30 | 8 | Yes |
Detailed Benchmark Studies
- IETF Benchmark Study:
- The IETF published a comprehensive study comparing Opus with other codecs, highlighting its superior performance in terms of audio quality and robustness to packet loss. IETF Opus Specification
- Mozilla Developer Network:
- Mozilla conducted internal benchmarks to evaluate Opus’s performance in Firefox, confirming its low latency and high audio quality. MDN Web Docs
- Xiph.Org Foundation:
- Xiph.Org, the developers behind Opus, provide detailed performance benchmarks demonstrating Opus’s efficiency and adaptability across various scenarios. Xiph.Org Opus
Notable Companies Using Opus
Several leading companies have adopted Opus for their communication needs, recognizing its advantages in audio quality and efficiency. Notable examples include:
- Zoom: The popular video conferencing platform uses Opus to ensure high-quality audio during calls and meetings .
- WhatsApp: Opus is employed in WhatsApp’s voice call feature, providing clear and reliable audio communication over variable network conditions .
- Discord: The voice, video, and text communication service for gamers uses Opus to deliver low-latency and high-quality voice chat .
- Mozilla: Firefox supports Opus for audio playback and real-time communication via WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) .
Conclusion
Opus stands out in the VoIP codec landscape due to its superior audio quality, low latency, and efficient bandwidth usage. Compared to traditional codecs like G.711 and G.729, and even modern ones like AAC, Opus offers significant advantages that can lead to cost savings for companies by reducing bandwidth requirements and minimizing the need for hardware upgrades. These benefits, coupled with its robustness in handling packet loss, make Opus an ideal choice for modern communication systems.
References
- Valin, J.-M., Vos, K., & Terriberry, T. (2012). Definition of the Opus Audio Codec. IETF. Retrieved from IETF Opus Specification
- Chen, J. (2019). Real-Time Communication with Opus. Retrieved from WebRTC
- Xiph.Org. (2020). Opus Codec Overview. Retrieved from Xiph.Org Opus
- Mozilla Developer Network. (2021). Opus Codec. Retrieved from MDN Web Docs
- Zoom Video Communications, Inc. (2023). Zoom Technical Overview. Retrieved from Zoom
- WhatsApp Inc. (2023). WhatsApp Voice Calling. Retrieved from WhatsApp
- Discord Inc. (2023). Discord Voice Chat. Retrieved from Discord
- Mozilla Foundation. (2023). Firefox and WebRTC. Retrieved from Mozilla
By adopting Opus, companies can achieve superior audio quality, improve user satisfaction, and realize significant cost savings, making it a compelling choice for modern VoIP applications.

![Freeswitch CI/CD with GitHub Actions, DroneCI [PART 2]](https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*rb4h_gy5QrVgDOZw)
