Understanding Jitter in VoIP: Root Causes and Technical Analysis

Voice over IP (VoIP) technology allows for the transmission of voice communications over the Internet. While it offers significant cost advantages and flexibility, it also introduces new technical challenges. One of the most critical issues in VoIP communication is jitter, which refers to the variation in packet arrival times.
High jitter can severely impact call quality, leading to choppy audio and poor user experience. In this article, we will explore the root causes of jitter in VoIP, including bandwidth issues and codec misconfiguration, and illustrate these concepts with detailed charts.
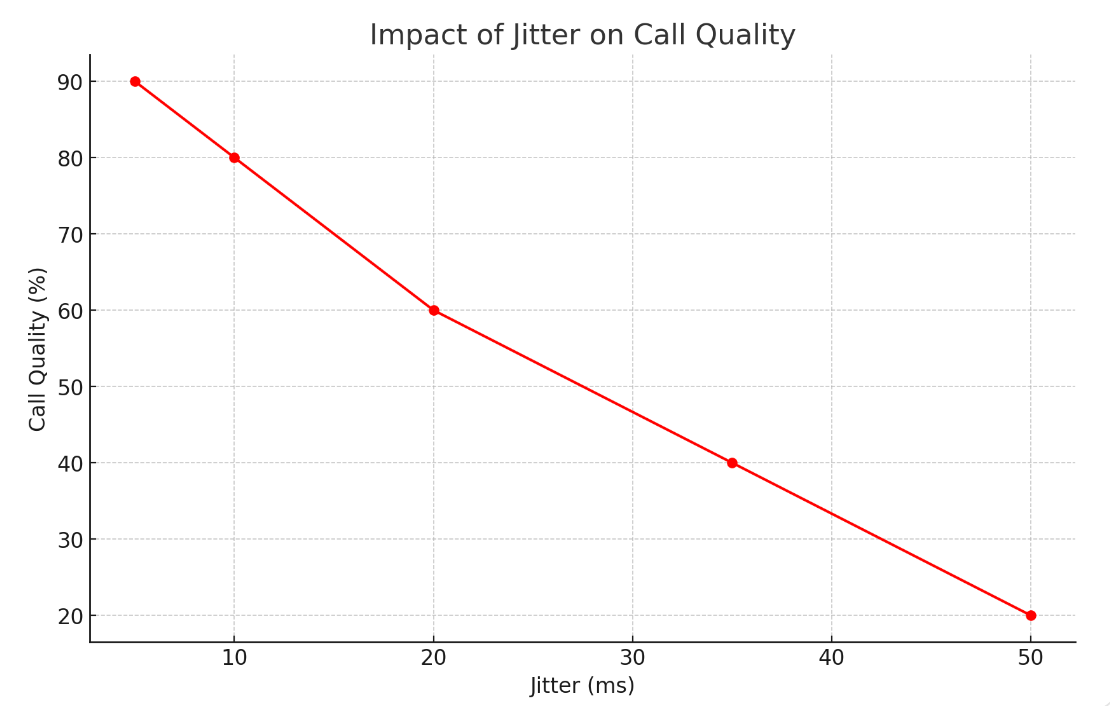
This graph illustrates that as jitter increases, the quality of the VoIP call decreases. High jitter leads to poor call quality, highlighting the importance of managing jitter to ensure clear and reliable voice communications.
Root Causes of Jitter in VoIP
- Network Congestion
Network congestion occurs when the demand for bandwidth exceeds the available capacity. This can happen due to excessive data traffic, inefficient network management, or bandwidth-heavy applications running concurrently with VoIP traffic.
Congestion causes packets to be delayed or dropped, leading to inconsistent arrival times and increased jitter. - Insufficient Bandwidth
Each VoIP call requires a certain amount of bandwidth to maintain quality. If the available bandwidth is insufficient, packets can be delayed as they wait for transmission opportunities.
Lack of bandwidth leads to packet queuing and delays, contributing to jitter. - Codec Configuration
Codecs compress and decompress voice signals for transmission over the network. Misconfigured codecs can lead to inefficient use of bandwidth and increased processing delays.
Using a high-compression codec on a network with adequate bandwidth can save bandwidth but might introduce processing delays. Conversely, using low-compression codecs on bandwidth-constrained networks increases congestion. - Network Hardware and Software Issues
Network devices such as routers and switches, as well as their firmware and configurations, can introduce delays. Issues like buffer overflows, firmware bugs, and misconfigurations can contribute to jitter.
Inefficient packet handling and delays at network devices lead to increased jitter. - Packet Routing
The path packets take from source to destination can affect their arrival times. Packets taking different routes can experience varying delays.
Variability in packet routes causes inconsistent packet arrival times, increasing jitter. - Wireless Networks
Wireless networks are more susceptible to interference, signal degradation, and variable latency compared to wired networks.
Wireless transmission issues lead to packet loss and delays, contributing to jitter.
To better understand how these factors impact VoIP quality, let's delve into some technical details and illustrate the concepts with charts.
Bandwidth and Jitter
Consider a network with varying bandwidth availability. In a scenario where the bandwidth is adequate, VoIP packets are transmitted smoothly with minimal delay. However, when bandwidth becomes constrained, packets experience delays due to queuing, leading to increased jitter.
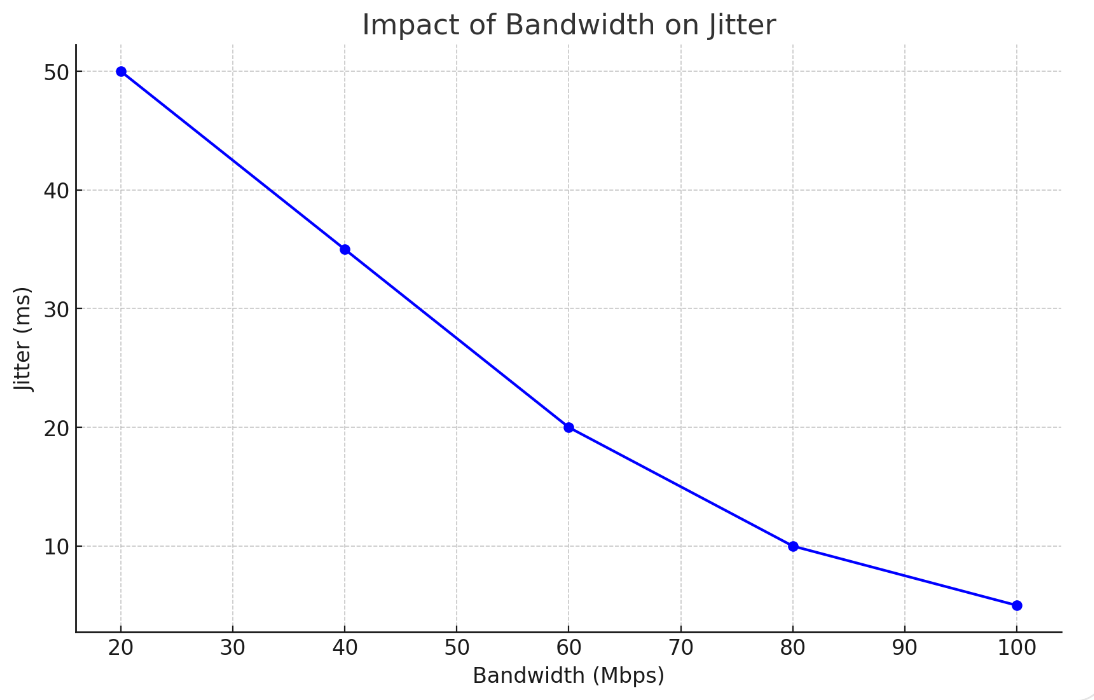
This chart shows a clear inverse relationship between bandwidth and jitter. As bandwidth decreases, jitter increases significantly, indicating the importance of adequate bandwidth for maintaining VoIP call quality.
Codec Configuration and Jitter
Different codecs have varying bandwidth requirements and processing delays. For instance, high-compression codecs like G.729 use less bandwidth but introduce more processing delay compared to low-compression codecs like G.711.

This chart illustrates the trade-off between bandwidth usage and jitter for different codecs. Codecs with lower bandwidth usage, such as G.729, tend to introduce higher jitter due to increased processing requirements.
Network Congestion and Jitter
Network congestion can be simulated by introducing varying levels of traffic load on a network and observing the resulting jitter.
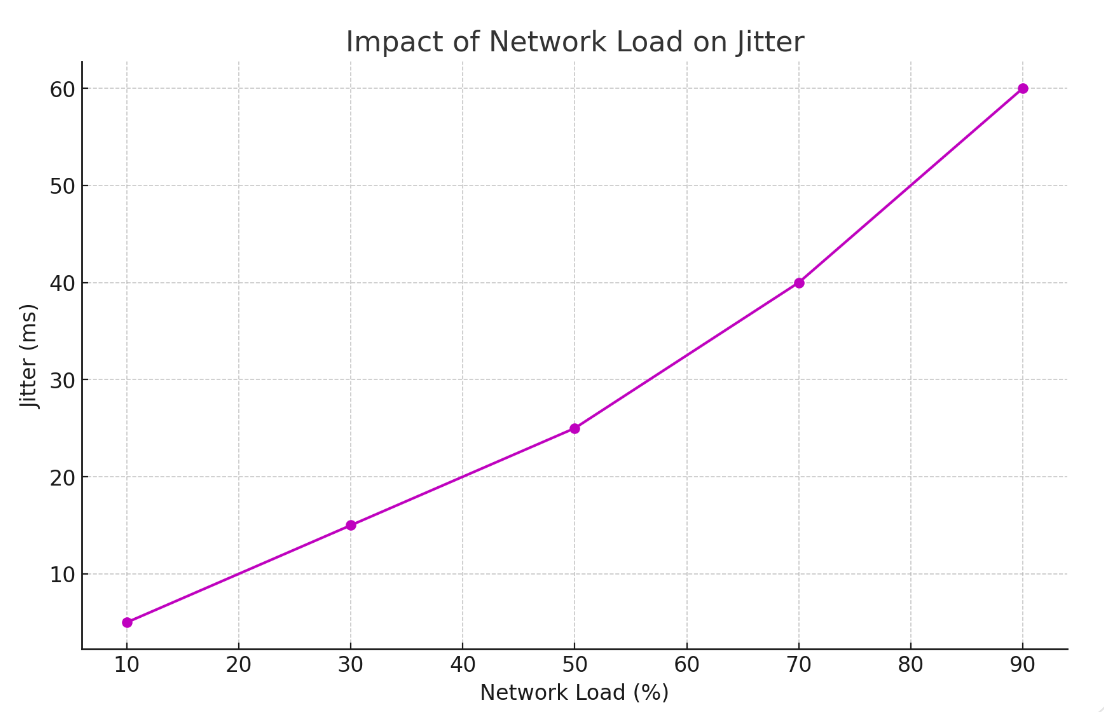
As network load increases, jitter increases dramatically. This highlights the impact of network congestion on VoIP quality and the importance of efficient network management.
Conclusion
Jitter in VoIP can arise from multiple sources, including network congestion, insufficient bandwidth, codec misconfiguration, hardware and software issues, packet routing, and the use of wireless networks. Understanding these root causes and their impact on jitter is crucial for maintaining high-quality VoIP communications.
By ensuring adequate bandwidth, properly configuring codecs, and managing network load, the effects of jitter can be minimized, leading to clearer and more reliable voice calls.

![Freeswitch CI/CD with GitHub Actions, DroneCI [PART 2]](https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*rb4h_gy5QrVgDOZw)
